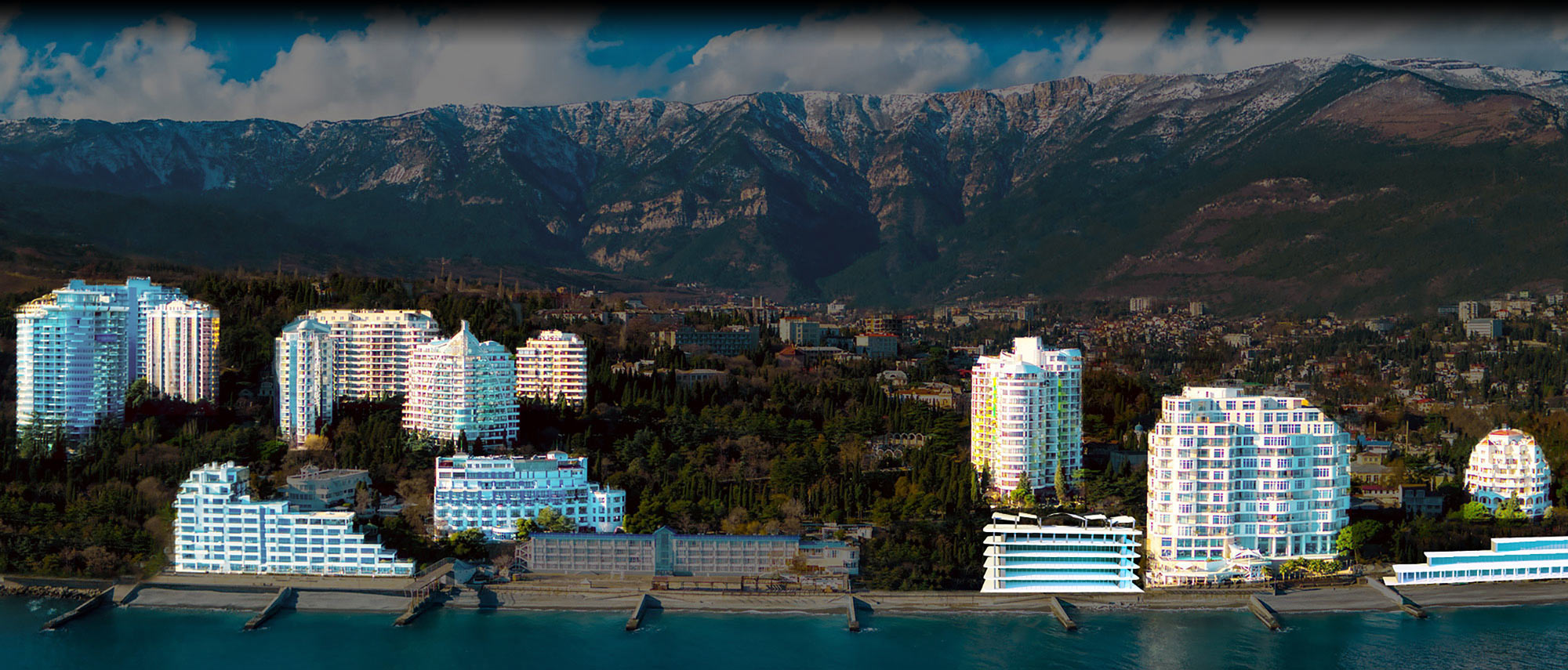
A safe haven is an investment expected to retain or increase value during market turbulence. The U.S. dollar is considered a haven during times of global economic uncertainty, so the demand for dollars often persists despite fluctuations in the performance of the U.S. economy. A country with a strong economy will attract investment from around the world. Investors will perceive safety and the ability to achieve an acceptable rate of return on investment. Since investors seek out the highest yield, an increase in investment, particularly from abroad, creates a strong capital account and a high demand for U.S. dollars. Kana Norimoto, fixed-income macro analyst at Fidelity, expects the dollar to remain strong as long as the US economy continues to outperform other big economies and the Federal Reserve continues to raise interest rates.
Images of U.S. currency and coins
- They were referred to as “greenbacks” because they were green in color.
- Since the discontinuation of all other types of notes (Gold Certificates in 1933, Silver Certificates in 1963, and United States Notes in 1971), US dollar notes have since been issued exclusively as Federal Reserve Notes.
- Among the countries using the U.S. dollar together with other foreign currencies and their local currency are Cambodia and Zimbabwe.
- While a strong dollar may hurt US stocks, it also makes international stocks a bargain for US investors who want to diversify their portfolios.
- While issuance of United States Notes ended in January 1971, existing United States Notes are still valid currency in the United States today, though rarely seen in circulation.
In 1971, the U.S. announced it would not freely convert dollars at the exchange rate with gold. In October 1976, the definition of the dollar in terms of gold was officially removed from statute and the USD and gold no longer had any link. The United States dollar, often referred to as the greenback, was created through the Coinage Act of 1792, which specified that a dollar of currency would be equal to between 371 and 416 grains of silver, and an “eagle” (US$10) at between 247 and 270 grains of gold.
Besides hurting earnings, a super-strong dollar can also hurt prices of US stocks and bonds by making them more expensive for big non-US institutional investors. Faced with higher prices, they may opt to invest their money elsewhere, dragging US markets downward in the process. Typically, if a country has relatively strong economic growth and low debt, its currency will be sought after in global markets which will cause its price to rise. On the other hand, countries whose growth is weak and debt is high may see less demand for their currencies and their value will lag those of countries with more robust economies. Part of the reason for the dollar’s strength is its role as the world’s reserve currency.
Silver certificates
Changes in the dollar’s value can have a big impact on a company’s international sales, since it can erode their competitiveness in any market whose currency is cheaper than the greenback. Each dollar is worth 100 cents and each dollar bill holds the same value as one hundred cents. Views expressed are as of the date indicated, based on the information available at that time, and may change based on market or other conditions. Unless otherwise noted, the opinions provided are those of the speaker or author and not necessarily those of Fidelity Investments or its affiliates.
Under the post-World War II Bretton Woods system, all other currencies were valued in terms of U.S. dollars and were thus indirectly linked to the gold standard. The need bitmex review for the U.S. government to maintain both a $35 per troy ounce (112.53 cents/gram) market price of gold and also the conversion to foreign currencies caused economic and trade pressures. By the early 1960s, compensation for these pressures started to become too complicated to manage. The term “U.S. dollar” refers to a specific denomination and the U.S. currency in general. It was initially traded as a coin worth its weight in silver or gold and then exchanged as a paper note redeemable in gold.
Pound hits post-Truss high as dollar weakens
This exchange also makes the value of their currency weaker, allowing their goods to seem cheaper. In addition to holding onto dollars, these countries buy Treasury notes, which helps make the dollar stronger. The USD’s relation to gold and its eventual delinking had a lengthy process.
That allows the U.S. to continue its role as the consumption engine that fuels world economies, even though it’s a debtor nation that borrows this money to consume. This also allows other countries to export to the U.S. and keep their economies growing. The good news for investors is a strong dollar can continue to benefit certain stocks that generate limited international revenue. Bank of America recently screened for S&P 500 stocks that have historically had the most positive correlation to the strength of the dollar over the past decade.
Banknotes
Whether it’s an overnight in Niagara or a safari in Namibia, you’re nearly certain to get more for less. The United States no longer produces the half-cent coin, the two-cent coin, the three-cent coin, the half-dime coin (different from the nickel), or the twenty-cent coin. On the reverse of the Great Seal stands an unfinished pyramid of 13 rows, symbolizing strength and duration.
For a more exhaustive discussion of countries using the U.S. dollar as official or customary currency, or using currencies which are pegged to the U.S. dollar, see International use of the U.S. dollar#Dollarization and fixed exchange rates and Currency substitution#US dollar. When the Federal Reserve makes a purchase, it credits the seller’s reserve account (with the Federal Reserve). This money is not transferred from any existing funds—it is at this point that the Federal Reserve has created new high-powered money.
Notes above the $100 denomination stopped being printed in 1946 and were officially withdrawn from circulation in 1969. These notes were used primarily in inter-bank transactions or by organized crime; it was the latter usage that prompted President Richard Nixon to issue an executive order in 1969 halting their use. Notes in denominations of $500, $1,000, $5,000, $10,000 (discontinued, but still legal tender); $100,000were all produced at one time; see large denomination bills in U.S. currency for details. With the exception of the $100,000 bill (which was only issued as a Series 1934 Gold Certificate and was never publicly circulated; thus it is illegal to own), these notes are now collectors’ items and are worth more than their face value to collectors. The U.S. dollar became an important international reserve currency after the First World War, and displaced the pound sterling as the world’s primary reserve currency by the Bretton Woods Agreement towards the end of the Second World War.
Those fluctuating currency values reflect how much the governments, companies, banks, and individual investors who buy and sell in global currency markets are willing to pay. Their views on the relative values of currencies mostly reflect where they believe they will get the best return bitbuy review on their investment. Currently printed denominations are $1, $2, $5, $10, $20, $50, and $100.
She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Wayne Duggan has a decade of experience covering breaking market news and providing analysis and commentary related to popular stocks. News & World Report and a regular contributor for Forbes Advisor and USA Today. Investors willing to take on more risk for more potential upside can also directly buy U.S. dollar futures or options contracts. Any investor trading these types of derivatives should understand how they work and the risks involved. The top stocks Bank of America found were helped by the rising dollar include Huntington Ingalls Industries (HII), Darden Restaurants (DRI) and Clorox (CLX).
Large numbers of these eight-real coins were captured during the Napoleonic Wars, hence their re-use by the Bank of England. They remained in use until 1811.[35][36] During World War II, when the U.S. dollar was (approximately) valued at five shillings, the half crown (2s 6d) acquired the nickname “half dollar” or “half a dollar” in the UK. Traders can follow the Dollar Index chart to see how the dollar fares against other currencies. A trader can develop a sense of the flow of dollars and form an insight on how best to select profitable trading positions by watching the patterns on the chart and listening to the major fundamental factors that affect supply and demand. A strong dollar can be bad news for U.S. companies that do business overseas.